Uncovering Attack Paths based on Misconfiguration
Filipi Pires
Head of Identity Threat Labs & Global Product Advocate
Abstract
Cybersecurity threats are continually evolving, demanding a proactive approach to safeguarding digital assets. One critical aspect of defense is comprehending and securing attack paths—the systematic routes malicious actors take to compromise systems, networks, or organizations. This article explores the concept of attack paths, shedding light on their components, significance, and strategies for fortifying cybersecurity defenses.
An attack path comprises reconnaissance, initial access, lateral movement, persistence, and exfiltration. Reconnaissance involves gathering intelligence about potential vulnerabilities, while initial access entails exploiting entry points. Lateral movement sees attackers navigating through networks, establishing persistence to maintain access, and concluding with data exfiltration.
Understanding attack paths is paramount for developing effective cybersecurity strategies. By dissecting potential routes, organizations can implement targeted security measures. These may include vulnerability management, access controls, monitoring and detection tools, user education, and robust incident response planning.
The role of a cybersecurity advocate is crucial in this context. Advocates bridge the gap between security teams and end-users, fostering a culture of security. They actively engage with internal stakeholders, represent the organization in external forums, and contribute to the development and enforcement of security policies. Additionally, cybersecurity advocates play a pivotal role in incident response, providing support and guidance during security incidents.
This article emphasizes the need for continuous cybersecurity education and training, with advocates developing and delivering programs to keep employees informed about evolving threats. Security advocacy campaigns, metrics, and reporting mechanisms further enhance organizational resilience by promoting a strong cybersecurity culture.
In conclusion, as cybersecurity threats persist, understanding and securing attack paths remain integral to fortifying defenses. This article advocates for a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that addresses vulnerabilities at each step of an attack path, ensuring organizations are well-equipped to protect against a dynamic and evolving threat landscape.
Introduction:
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, staying ahead of potential threats requires a proactive approach. One crucial aspect of this approach is understanding and securing attack paths. An attack path is the sequence of steps an attacker might take to exploit vulnerabilities and compromise a system, network, or organization. This article delves into the concept of attack paths, their significance, and strategies to enhance cybersecurity defenses.
What is an Attack Path?
An attack path is essentially the roadmap a malicious actor follows to achieve their objectives. It involves identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities in a systematic manner. These vulnerabilities can exist in various elements of a system, including software, hardware, network configurations, and even human factors like misconfiguration, social engineering and others.
Components of an Attack Path:
- Reconnaissance: The first step in any attack path involves gathering information about the target. This can include identifying potential vulnerabilities, mapping the network architecture, and profiling potential targets within the organization.
- Initial Access: Once the reconnaissance is complete, the attacker seeks a way to gain initial access to the system. This could involve exploiting software vulnerabilities, using phishing attacks, or compromising user credentials.
- Lateral Movement: With an initial foothold, the attacker moves laterally through the network, exploring and exploiting additional vulnerabilities. This might involve escalating privileges, compromising other systems, and spreading across the organization.
- Persistence: To maintain access and avoid detection, attackers often establish persistence by creating backdoors, installing malware, or manipulating system configurations.
- Exfiltration: The final step in many attack paths involves stealing or manipulating data. Attackers aim to achieve their ultimate goals, such as theft of sensitive information, financial gain, or disruption of operations.
Significance of Understanding Attack Paths:
Understanding attack paths is crucial for developing effective cybersecurity strategies. By comprehending how attackers might navigate through a system, organizations can implement targeted security measures to disrupt these paths. This involves a combination of technological solutions, regular vulnerability assessments, and user education to mitigate human-related risks.
Securing Attack Paths:
- Vulnerability Management: Regularly identify and patch software vulnerabilities to eliminate potential entry points for attackers.
- Access Control: Implement strong access controls and privilege management to limit lateral movement within the network.
- Monitoring and Detection: Employ robust monitoring tools to detect unusual activities or patterns that may indicate a potential attack in progress.
- User Education: Educate users about security best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts and practicing good password hygiene, to reduce the human element in attack paths.
- Incident Response Planning: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to effectively contain and mitigate the impact of a security incident.
Understanding HVT and Attack Vector
In the context of United States military terminology, a High-Value Target (HVT) refers to an individual or asset essential for the successful execution of an enemy commander's mission. Within your organization, consider which staff members possess the capability to grant access to vital information or systems, and whose compromise could potentially result in a singular point of failure. Identify those individuals whose successful targeting in an attack poses a high-impact risk to the organization.
High-Value Targets (HVTs) typically encompass individuals holding prominent roles such as those in the C-Level, board members, senior executive management, executive assistants, or personnel with elevated access privileges to organizational and technological assets. Alternatively, HVTs may constitute entire teams engaged in sensitive or high-stakes projects. Additionally, an individual could transition into an HVT during a defined period, particularly when actively involved in a critical project crucial for the organization.
Another concept we know as Attack Vector which refers to the specific technique employed by cyber attackers to breach a system. It's important to distinguish between attack vectors and attack surfaces, as the latter encompasses all potential points where adversaries may attempt unauthorized entry into a network or system. While these terms are occasionally conflated, understanding their distinct definitions is crucial for effective cybersecurity analysis and defense.
Malware, ransomware, and phishing stand as typical instances of prevalent attack vectors. Human errors contributing to the formation of attack vectors involve actions such as:
- Maintaining weak credentials;
- Employing ‘poor’ encryption practices;
- Misconfigurations;
- Granting access to sensitive information through privilege escalation;
In this sense, an Attack Vector serves as the entry point or doorway, while an Attack Path functions as a map detailing the adversary's entry through the door and their subsequent movements within the system.
AWS IAM
In summary, AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management) is a web service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that enables you to securely control access to AWS services and resources. IAM is a fundamental component of AWS security, allowing you to manage users, groups, roles, and their permissions within your AWS environment.
In AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), policies are JSON documents that define permissions and can be attached to IAM users, groups, and roles. Each IAM policy has a version associated with it, which indicates the syntax and structure of the policy language.
Exploitation based on Misconfiguration
In the complex landscape of Cloud, IT systems and networks, the configuration of various components is a critical aspect of maintaining security and operational integrity. Misconfiguration occurs when settings, permissions, or parameters are not appropriately defined, leaving systems susceptible to exploitation by attackers.
Common scenarios of misconfiguration encompass a wide range of IT environments:
- Cloud Services:
- Misconfigurations in cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud can expose sensitive data, allow unauthorized access, or lead to unintended consequences.
- User Access Controls:
- Mismanagement of user permissions and access controls can lead to unauthorized users gaining excessive privileges, potentially compromising the confidentiality and integrity of data.
- Web Servers and Applications:
- Improperly configured web servers, databases, and application servers may introduce vulnerabilities, potentially enabling attackers to execute malicious activities or gain unauthorized access.
- Network Devices:
- Misconfigurations in routers, switches, and firewalls can result in network vulnerabilities, allowing unauthorized access, data leakage, or disruptions in service.
- Security Software:
- Misconfigured security tools, such as intrusion detection systems or firewalls, may fail to provide effective protection, leaving gaps in the overall security posture.
The consequences of misconfiguration can be severe, including data breaches, service disruptions, financial losses, and damage to an organization's reputation. It underscores the importance of implementing robust configuration management practices, conducting regular audits, and staying informed about best practices in cybersecurity to prevent and mitigate the risks associated with misconfigurations.
Misconfiguration in IAM services
Misconfigurations in Identity and Access Management (IAM) services, such as AWS IAM in cloud environments, can introduce significant security risks. IAM misconfigurations typically involve errors in defining user permissions, roles, policies, or other access controls. These misconfigurations can result in unintended access, data exposure, and potential security breaches. Common issues include overly permissive policies, incorrect trust relationships, and inadequate authentication controls. To mitigate these risks, organizations should implement thorough IAM policies, regularly audit configurations, and stay informed about best practices for secure identity and access management in their cloud environments.
Misconfiguration Attack based on Actions in AWS
Important Note
All these attacks can happen after you or the attacker get the access on AWS Secrets and AWS Keys to logging on AWS CLI.
AWS Attack based on Create Policy Version
A potential security risk arises from the iam:CreatePolicyVersion action, granting an attacker the ability to generate a new version of an IAM policy they have access to. This permits them to define customized permissions. Although setting a new policy version as the default typically necessitates the iam:SetDefaultPolicyVersion permission, an exploitable flag (--set-as-default) can be included during new policy version creation to automatically designate it as the default version. Importantly, the use of this flag doesn't require the iam:SetDefaultPolicyVersion permission.
Let’s see what happens when the User doesn’t have this Permission, let’s try some commands:
- aws iam list-users
- aws iam list-policies
- aws iam list-group
As you can see the access was denied, because the user doesn’t have this permission.
Let’s create this New Policy using this Action
After that, as you can see below, the policy called - PoC-AttackModel is created, this attack can be done only using iam:CreatePolicyVersion is not necessary add the iam:CreatePolicy as you see in the print the create policy
What are the next steps? You can do a simple research on the internet such as:
“aws iam full access policy”
“AWS CLI how to create new policy version”
After that you have all steps to perform this attack, you just need to create a full access.
Now, you just need to set the command
aws iam create-policy-version –policy-arn target_policy_arn –policy-document file://path/to/user/policy.json –set-as-default
Let’s see what happened in the AWS Console after the attack.
Now, you have full control over the AWS IAM service, This method of privilege escalation has the capability to grant a user complete administrator access to the AWS account.
After that you can set simple enumeration commands such as:
- aws iam list-users
- aws iam list-group
- aws iam list-policies
Now, we know the impact about the Misconfiguration in the Cloud, Mapping misconfigurations in Identity and Access Management (IAM) is crucial for ensuring the security and integrity of cloud environments. IAM misconfigurations can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential compromise of critical resources.
Let’s see an OpenSource Project that you can use to have this visibility in a graph way.
Cartography is a Python tool that consolidates infrastructure assets and the relationships between them in an intuitive graph view powered by a Neo4j database.
Let’s execute in our demo lab to see possible users that can suffering this attack
MATCH(principal:AWSPrincipal)-->(policy:AWSPolicy)-->(statement:AWSPolicyStatement) WHERE "iam:CreatePolicy" IN statement.action RETURN principal, policy, statement
How can I mitigate it?
You can use multiplus aways to solve it, you need to have visibility, and would like to present to you this community project using Cloud Infrastructure Entitlements Management (CIEM) serves the purpose of overseeing access in both cloud and multi-cloud environments. It operates on the principle of Least Privilege, benefiting organizations seeking to mitigate risks such as malicious attacks and data breaches resulting from overly permissive permissions within this infrastructure. A CIEM solution facilitates the removal of unnecessary entitlements, providing centralized visibility and control over permissions within the cloud environment. Leveraging artificial intelligence, a CIEM solution can intelligently analyze a company's cloud environments, identifying and diminishing cybersecurity risks by assessing exposure levels. In essence, CIEM acts as a comprehensive tool to enhance security and streamline permissions in cloud infrastructures.
We are inviting you to have first-hand access to our new cloud security platform and participate in our beta users program. If you are an Information Security professional with experience in IAM and wish to participate in the construction of an innovative project, come build with us
https://senhasegura.com/build-with-us
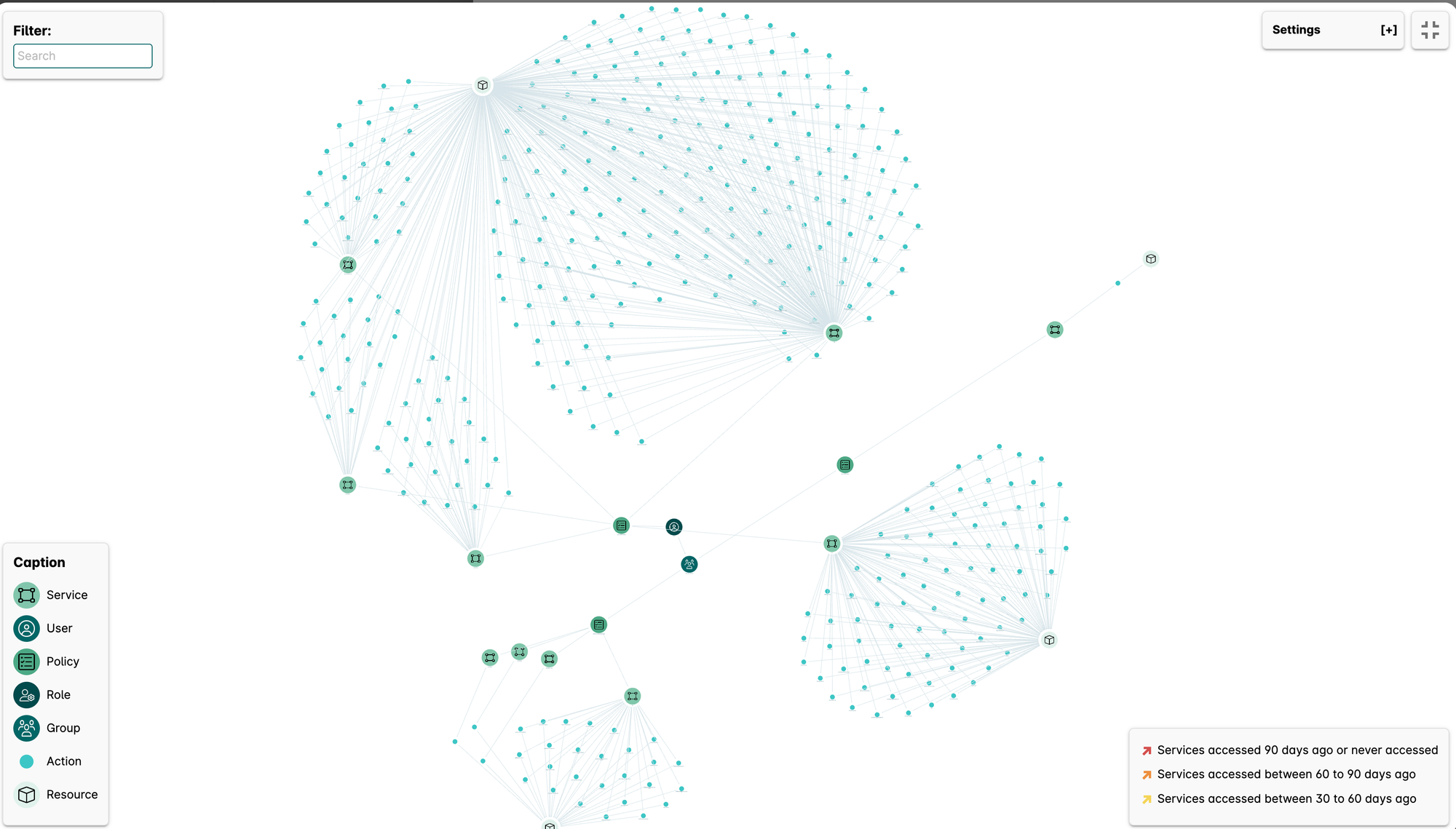
Access Path visibility
Remember the attack mentioned in this article? - Create Policy Version? Take a look at this user!
Conclusion:
In the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity, the comprehension and fortification of attack paths emerge as critical imperatives for organizations striving to safeguard their digital assets. The exploration of attack paths in this article illuminates the intricacies of the routes malicious actors traverse to exploit vulnerabilities systematically. As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations must adopt a proactive and comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that addresses potential weaknesses along every step of an attack path.
The components of an attack path—reconnaissance, initial access, lateral movement, persistence, and exfiltration—underscore the complexity of cyber threats. Recognizing these components allows organizations to implement targeted security measures, creating a robust defense against potential breaches. Vulnerability management, access controls, monitoring and detection tools, user education, and incident response planning collectively form a multi-faceted approach to thwart cyber adversaries.
In conclusion, the battle against cyber threats requires a holistic and proactive approach. Understanding and securing attack paths serve as foundational elements in this ongoing struggle. By embracing these concepts and fostering a cybersecurity-aware culture, organizations position themselves not just to defend against current threats but to adapt and thrive in an environment where the only constant is change. In this ever-evolving landscape, the fortification of attack paths is not merely a defensive strategy; it is a proactive stance against the relentless tide of cyber threats.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, understanding and securing attack paths is essential for organizations to stay resilient. By adopting a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that addresses potential vulnerabilities at each step of an attack path, businesses can significantly enhance their overall security posture and protect against a wide range of cyber threats.
In our next articles, we will go into more detail about the impacts of other actions that AWS has, in addition, we will be doing research on other misconfigurations in different cloud providers, besides to starting lines of research into cross-platform attack paths
References:
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/aws-managed-policy/latest/reference/IAMFullAccess.html
- https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/aws-privilege-escalation-methods-mitigation/
- https://www.xmcyber.com/blog/attack-path-vs-attack-vector-important-differences-you-need-to-know/
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/access_policies.html
- https://github.com/lyft/cartography

